Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurements Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instrument, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
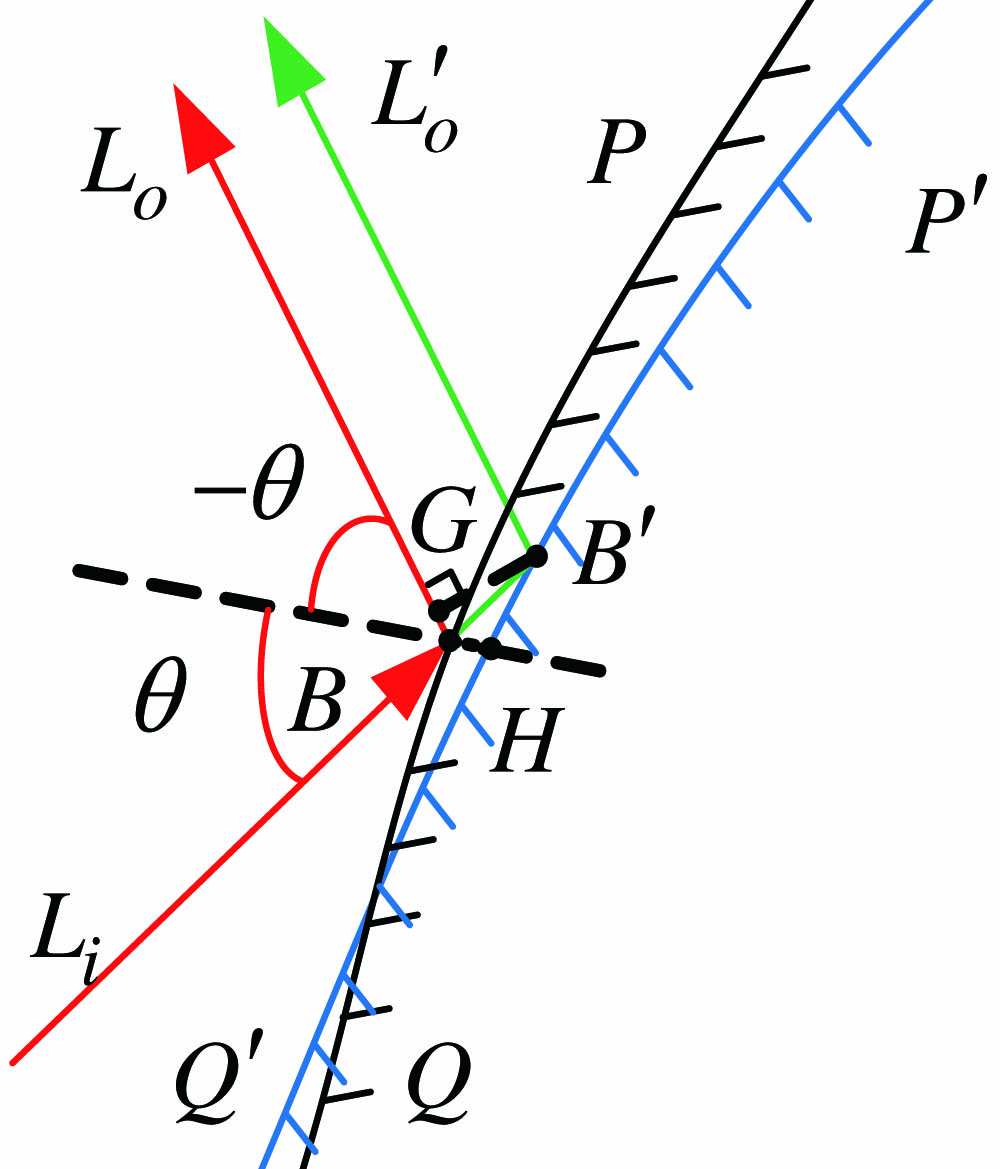
Freeform surfaces are difficult to manufacture due to their lack of rotational symmetry. To reduce the requirements for manufacturing precision, a design method is proposed for freeform reflective-imaging systems with low surface-figure-error sensitivity. The method considers both the surface-figure-error sensitivity and optical specifications, which can design initial systems insensitive to surface figure errors. Design starts with an initial planar system; the surface-figure-error sensitivity of the system is reduced during construction. The proposed method and another that is irrelevant to figure-error sensitivity are used to design a freeform off-axis three-mirror imaging system. Comparison of the sensitivities of the two systems indicates the superiority of our proposed method.
220.4830 Systems design 080.4228 Nonspherical mirror surfaces 220.4610 Optical fabrication 080.4035 Mirror system design Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(9): 092201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Med-X Research Institute and School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200030, P.R. China
2 Department of Immunology and Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular, Virology of MOE/MOH, School of Basic Medical Sciences, and Biotherapy Research Centre, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, P.R. China
3 Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan 250030, P.R. China
T-cell activation requires the formation of the immunological synapse (IS) between a T-cell and an antigen-presenting cell (APC) to control the development of the adaptive immune response. However, calcium release, an initial signal of T-cell activation, has been found to occur before IS formation. The mechanism for triggering the calcium signaling and relationship between calcium release and IS formation remains unclear. Herein, using live-cell imaging, we found that intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), an essential molecule for IS formation, accumulated and then was depleted at the center of the synapse before complete IS formation. During the process of ICAM-1 depletion, calcium was released. If ICAM-1 failed to be depleted from the center of the synapse, the sustained calcium signaling could not be induced. Moreover, depletion of ICAM-1 in ISs preferentially occurred with the contact of antigen-specific T-cells and dendritic cells (DCs). Blocking the binding of ICAM-1 and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), ICAM-1 failed to deplete at the center of the synapse, and calcium release in T-cells decreased. In studying the mechanism of how the depletion of ICAM-1 could influence calciumrelease in T-cells, we found that the movement of ICAM-1 was associated with the localization of LFA-1 in the IS, which affected the localization of calcium microdomains, ORAI1 and mitochondria in IS. Therefore, the depletion of ICAM-1 in the center of the synapse is an important factor for an initial sustained calcium release in T-cells.
T-cell activation immunological synapse ICAM-1 calcium signaling Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2018, 11(2): 1750015





